
When you plan to wire an entire building, you will want to save money whenever you can. Despite its cons, the THHN is still very popular because it is cheaper. It becomes an issue for some people, especially those who want to maximize saving time and energy during installation. Since this type uses nylon coating, it is not extremely flexible. When the insulation in THHN burns, it releases toxic smoke. It is important in electrical properties to determine its amp rating.Ī negative effect of having a thin insulation layer is frequent current leaking, leading to a breakdown. If you think about distinguishing this from other types, you will observe its PVC insulation. Several options of this type carry a dual rating cable, which you can identify by a THHN / THWN marking. THHN rates at 75☌ in a wet location or 90☌ in a dry location. It uses either aluminum or copper as the conductive material.įinally, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) wraps the conductive material and serves as insulation. Depending on the size, it comes in either a stranded or a solid wire. You can find this product in almost any commercial or residential building. The Thermoplastic High-Heat Nylon-coated wire is probably the more common option between the two. Thermoplastic High-Heat Nylon-coated (THHN) You can still find both across different infrastructures. The Thermoplastic Heat and Water-Resistant Nylon-coated wire is a better version of the THHN. The THWN can operate in an environment similar to the THHN without additional accessories. It stands for “Thermoplastic Heat and Water-resistant Nylon-coated.” Suppose you think about how these two are different. The most common types are the Thermoplastic High-Heat Nylon-coated (THHN) and THWN. When looking at electrical wires, manufacturers use different types of material for the coating. For example, a 12-gauge option can carry a higher amp than an 18-rated one. It means a higher AWG value would mean a smaller size. The table below shows that the AWG value is opposite the diameter.
#Amp wire gauge chart install#
If you plan to install anything involving electricity, always call for a professional electrician to handle the work for you. This section only serves as a guide when looking at a gauge chart.
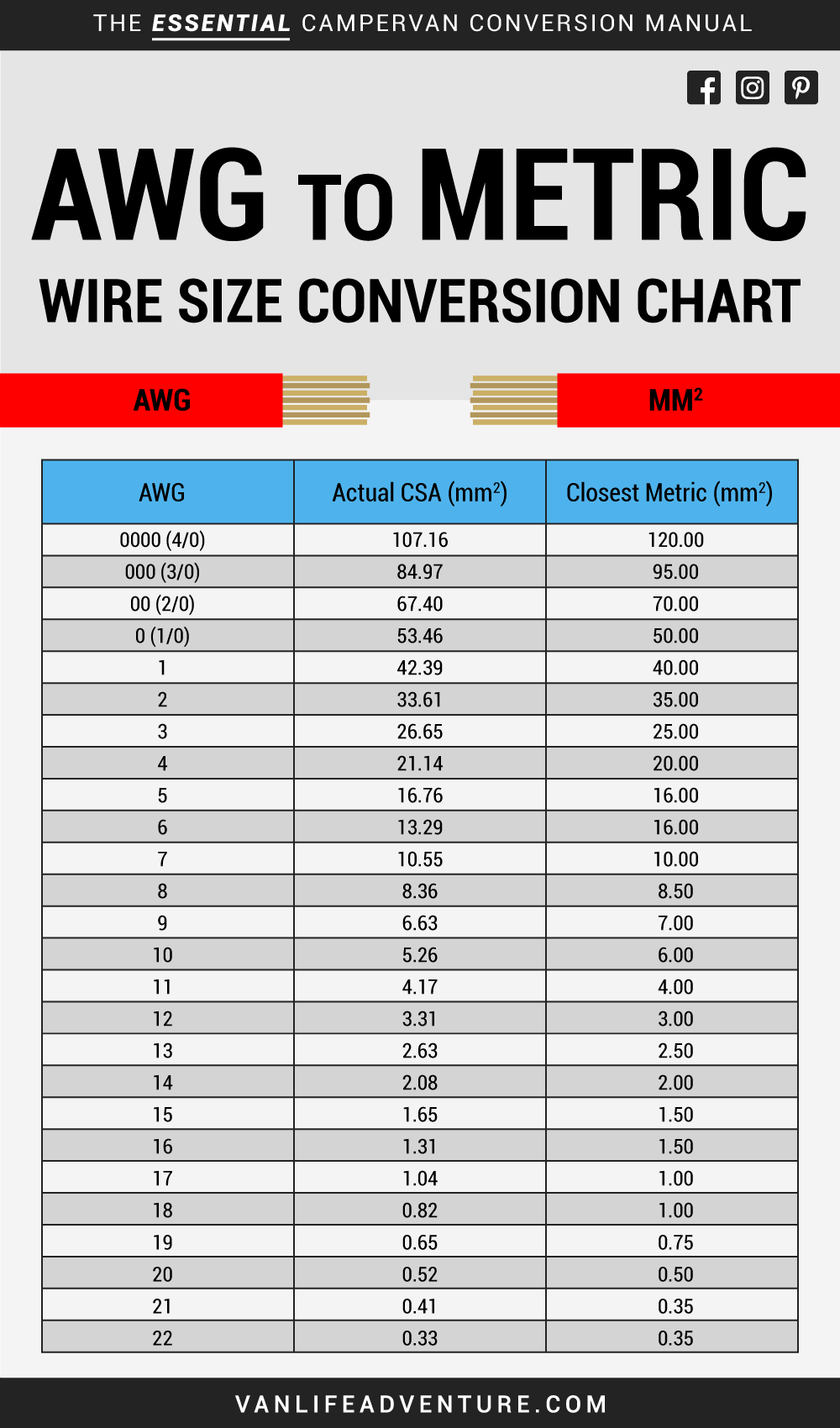
The 4 gauge wire amp rating is 85 amps for copper, with 167☏ ambient temperature.The 6 gauge wire amp rating is 65 amps for copper, with 167☏ ambient temperature.From it, you can see a list of things, including:

The NEC, THHN, & AWG wire gauge amp chart is the easiest way to see the amp rating for different wire thicknesses. We will be going through the different products in the following sections using the American wire gauge system. Its size greatly depends on other things, such as the electrical current passing through. Most people would think that it does not matter and is pure aesthetics. If you have been to an electrical store, you will notice electrical wires come in several sizes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
